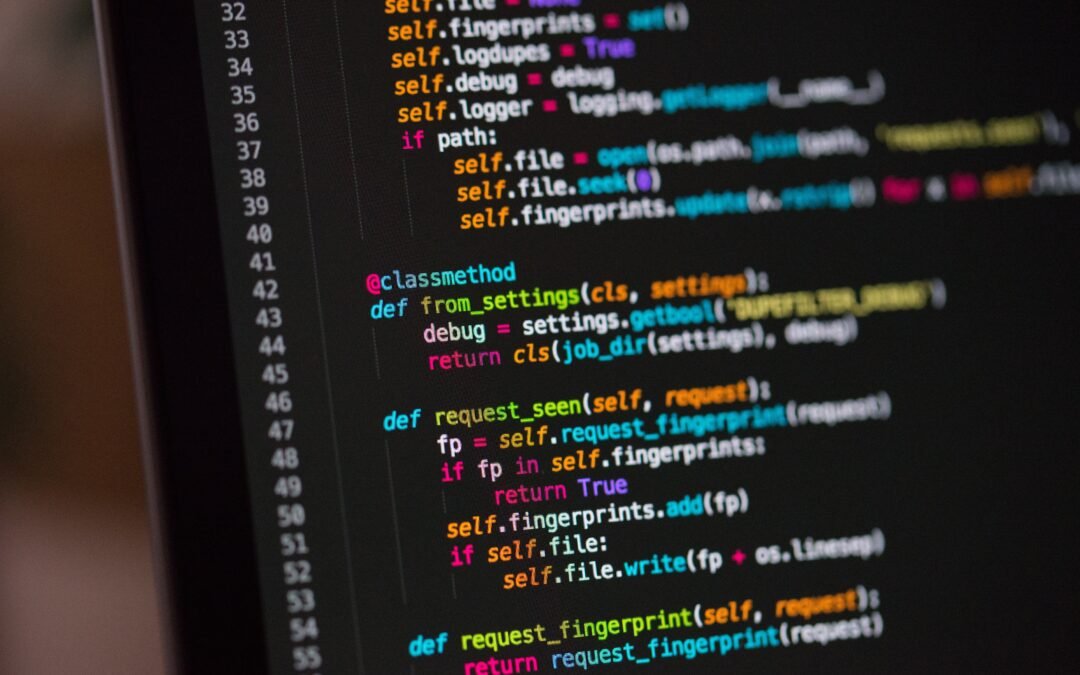
package length;
public class StringLength {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str =”Jesus is my Lord”;
int count = 0;
for(int i=0; i<str.length(); i++) {
if(str.charAt(i)!= ‘ ‘) {
count++;
}
}
System.out.println(“No of characters: ” +count);
}
}
Output: No of characters: 13
Java8 Tutorial
Example 1
package tutorial;
public class Training {
public void train() {
System.out.println(“Welcome to Greenwich Business School!”);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Training training = new Training();
training.train();
}
}
// Output: Welcome to Greenwich Business School!
Example 2
package game;
interface FootBall{
void kickBall();
}
public class Soccer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//lambda expression
FootBall footBall=()->
System.out.println(“Is a GOAL!!”);
footBall.kickBall();
};
}
// Output: Is a GOAL!!
Example 3
package game;
interface FootBall{
//void kickBall();
void score(int input);
}
public class Soccer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//lambda expression
/*FootBall footBall=()->
System.out.println(“Is a GOAL!!”);
footBall.kickBall();*/
FootBall footBall=(input)->
System.out.println(“Result: ” +input);
footBall.score(0);
};
}
//Output: Result: 0
Example
package game;
interface FootBall{
//void kickBall();
//void score(int input);
int scores(int i1, int i2);
}
public class Soccer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//lambda expression
/*FootBall footBall=()->
System.out.println(“Is a GOAL!!”);
footBall.kickBall();*/
/*FootBall footBall=(input)->
System.out.println(“Result: ” +input);
footBall.score(0);*/
FootBall footBall=(i1, i2)->{
return i1-i2;
};
System.out.println(footBall.scores(4, 3));
}
}
//Output: 1
package game;
interface FootBall{
//void kickBall();
//void score(int input);
int scores(int i1, int i2);
}
public class Soccer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//lambda expression
/*FootBall footBall=()->
System.out.println(“Is a GOAL!!”);
footBall.kickBall();*/
/*FootBall footBall=(input)->
System.out.println(“Result: ” +input);
footBall.score(0);*/
FootBall footBall=(i1, i2)->i1-i2;
System.out.println(footBall.scores(6, 3));
}
}
//Output: 3
Example of if statement
package game;
interface FootBall{
//void kickBall();
//void score(int input);
int scores(int i1, int i2);
}
public class Soccer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//lambda expression
/*FootBall footBall=()->
System.out.println(“Is a GOAL!!”);
footBall.kickBall();*/
/*FootBall footBall=(input)->
System.out.println(“Result: ” +input);
footBall.score(0);*/
FootBall footBall=(i1, i2)->{
if(i1 > i2) {
throw new RuntimeException(“message”);
}else{
return i1-i2;
}
};
System.out.println(footBall.scores(6, 14));
}
}
//Output: -8
}
}
String Length
package length;
public class StringLength {
interface LengthOfString {
int getLength(String s);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LengthOfString strLength = (String s) -> s.length();
System.out.println(strLength.getLength(“I son of God”));
}
}
package length;
public class StringLength {
interface LengthOfString {
int getLength(String s);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LengthOfString strLength = (s) -> s.length();
System.out.println(strLength.getLength(“I son of God”));
}
}
Shortest and more appropriate way of coding spring length
package length;
public class StringLength {
interface LengthOfString {
int getLength(String s);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LengthOfString strLength = s-> s.length();
System.out.println(strLength.getLength(“I son of God”));
}
}
//Output: 12
Anonymous Example
package game;
public class Scoreable {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread thread = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(“Scored on extra time”);
}
});
thread.run();
}
}
//Output: Scored on extra time
package game;
public class Scoreable {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread thread = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(“Scored on extra time”);
}
});
thread.run();
Thread myLambda = new Thread(() -> System.out.println(“Lambda without argument”));
myLambda.run();
}
}
//Output:
Scored on extra time
Lambda without argument
Practise Exercise to print names
package practise;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.List;
public class Exercise1Solution {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Person> people = Arrays.asList(
new Person(“John”, “Doe”, 25),
new Person(“Peter”, “Jones”, 23),
new Person(“Joseph”, “Golden”, 26),
new Person(“John”, “David”, 25),
new Person(“David”, “Paul”, 22)
);
//Sort list by lastname
Collections.sort(people, new Comparator<Person>() {
@Override
public int compare(Person o1, Person o2) {
return o1.getLastName().compareTo(o2.getLastName());
}
});
//Display list
printAll(people);
//Display lastname with D
lastNameBeginningWithD(people);
}
private static void lastNameBeginningWithD(List<Person> people) {
for(Person p : people) {
if(p.getLastName().startsWith(“D”)) {
System.out.println(p);
}
}
}
private static void printAll(List<Person> people) {
for(Person p : people) {
System.out.println(p);
}
}
}
//Output:
Person [firstName=John, lastName=David, age=25]
Person [firstName=John, lastName=Doe, age=25]
Person [firstName=Joseph, lastName=Golden, age=26]
Person [firstName=Peter, lastName=Jones, age=23]
Person [firstName=David, lastName=Paul, age=22]
Person [firstName=John, lastName=David, age=25]
Person [firstName=John, lastName=Doe, age=25]
Implementation using Java 8
package practise;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.List;
public class Exercise1SolutionJava8 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Person> people = Arrays.asList(
new Person(“John”, “Doe”, 25),
new Person(“Peter”, “Jones”, 23),
new Person(“Joseph”, “Golden”, 26),
new Person(“John”, “David”, 25),
new Person(“David”, “Paul”, 22)
);
//Sort list by lastname
Collections.sort(people, (p1, p2) -> p1.getLastName().compareTo(p2.getLastName()));
//Display list
printAll(people);
//Display lastname with D
lastNameBeginningWithD(people);
}
private static void lastNameBeginningWithD(List<Person> people) {
for(Person p : people) {
if(p.getLastName().startsWith(“D”)) {
System.out.println(p);
}
}
}
private static void printAll(List<Person> people) {
for(Person p : people) {
System.out.println(p);
}
}
}
//Output:
Person [firstName=John, lastName=David, age=25]
Person [firstName=John, lastName=Doe, age=25]
Person [firstName=Joseph, lastName=Golden, age=26]
Person [firstName=Peter, lastName=Jones, age=23]
Person [firstName=David, lastName=Paul, age=22]
Person [firstName=John, lastName=David, age=25]
Person [firstName=John, lastName=Doe, age=25]
Java 8: lambda Expression
package practise;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
public class Exercise1Solution {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Person> people = Arrays.asList(
new Person(“John”, “Doe”, 25),
new Person(“Peter”, “Jones”, 23),
new Person(“Joseph”, “Golden”, 26),
new Person(“John”, “David”, 25),
new Person(“David”, “Paul”, 22)
);
//Sort list by lastName
Collections.sort(people, (p1, p2)->p1.getLastName().compareTo(p2.getLastName()));
//Display list
System.out.print(“Print all people”);
printConditionally(people, p -> true);
//Display lastname with D
System.out.println(“Print all lastNames beginning with a ‘D'”);
printConditionally(people, p->p.getLastName().startsWith(“D”));
System.out.println(“Print all person with the firstname beginning with ‘J'”);
printConditionally(people, p->p.getFirstName().startsWith(“J”));
}
private static void printConditionally(List<Person> people, Condition condition) {
for(Person p : people) {
if(condition.test(p)) {
System.out.println(p);
}
}
}
/*
private static void printAll1(List<Person> people) {
for(Person p : people) {
System.out.println(p);
}
}
private static void printAll(List<Person> people) {
for(Person p : people) {
System.out.println(p);
}
}
*/
interface Condition {
boolean test(Person p);
}
}
Output:
Print all people
Person [firstName=John, lastName=David, age=25]
Person [firstName=John, lastName=Doe, age=25]
Person [firstName=Joseph, lastName=Golden, age=26]
Person [firstName=Peter, lastName=Jones, age=23]
Person [firstName=David, lastName=Paul, age=22]
Print all lastNames beginning with a ‘D’
Person [firstName=John, lastName=David, age=25]
Person [firstName=John, lastName=Doe, age=25]
Print all person with the firstname beginning with ‘J’
Person [firstName=John, lastName=David, age=25]
Person [firstName=John, lastName=Doe, age=25]
Person [firstName=Joseph, lastName=Golden, age=26]
Lambda Expression – Predicate
package practise;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
import java.util.function.Predicate;
public class Exercise1Solution {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Person> people = Arrays.asList(
new Person(“John”, “Doe”, 25),
new Person(“Peter”, “Jones”, 23),
new Person(“Joseph”, “Golden”, 26),
new Person(“John”, “David”, 25),
new Person(“David”, “Paul”, 22)
);
//Sort list by lastName
Collections.sort(people, (p1, p2)->p1.getLastName().compareTo(p2.getLastName()));
//Display list
System.out.print(“Print all people”);
printConditionally(people, p -> true);
//Display lastName with D
System.out.println(“Print all lastNames beginning with a ‘D'”);
printConditionally(people, p->p.getLastName().startsWith(“D”));
System.out.println(“Print all person with the firstname beginning with ‘J'”);
printConditionally(people, p->p.getFirstName().startsWith(“J”));
}
private static void printConditionally(List<Person> people, Predicate <Person> predicate) {
for(Person p : people) {
if(predicate.test(p)) {
System.out.println(p);
}
}
}
/*
private static void printAll1(List<Person> people) {
for(Person p : people) {
System.out.println(p);
}
}
private static void printAll(List<Person> people) {
for(Person p : people) {
System.out.println(p);
}
}
*/
interface Condition {
boolean test(Person p);
}
}
Output:
Print all peoplePerson [firstName=John, lastName=David, age=25]
Person [firstName=John, lastName=Doe, age=25]
Person [firstName=Joseph, lastName=Golden, age=26]
Person [firstName=Peter, lastName=Jones, age=23]
Person [firstName=David, lastName=Paul, age=22]
Print all lastNames beginning with a ‘D’
Person [firstName=John, lastName=David, age=25]
Person [firstName=John, lastName=Doe, age=25]
Print all person with the firstname beginning with ‘J’
Person [firstName=John, lastName=David, age=25]
Person [firstName=John, lastName=Doe, age=25]
Person [firstName=Joseph, lastName=Golden, age=26]
Functional Interface Example
package practise;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.function.Consumer;
import java.util.function.Predicate;
public class FunxrionalInterfacePractise1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Person> people = Arrays.asList(
new Person(“John”, “Doe”, 25),
new Person(“Peter”, “Jones”, 23),
new Person(“Joseph”, “Golden”, 26),
new Person(“John”, “David”, 25),
new Person(“David”, “Paul”, 22)
);
//Sort list by lastName
Collections.sort(people, (p1, p2)->p1.getLastName().compareTo(p2.getLastName()));
//Display list
System.out.print(“Print all people”);
performConditionally(people, p -> true, p -> System.out.println(p));
//Display lastName with D
System.out.println(“Print all lastNames beginning with a ‘D'”);
performConditionally(people, p->p.getLastName().startsWith(“D”),p -> System.out.println(p));
System.out.println(“Print all person with the firstname beginning with ‘J'”);
performConditionally(people, p->p.getFirstName().startsWith(“J”),p -> System.out.println(p));
}
private static void performConditionally(List<Person> people, Predicate<Person>predicate, Consumer consumer) {
for(Person p : people) {
if(predicate.test(p)) {
consumer.accept(p);
}
}
}
interface Condition {
boolean test(Person p);
}
}
Output:
Print all peoplePerson [firstName=John, lastName=David, age=25]
Person [firstName=John, lastName=Doe, age=25]
Person [firstName=Joseph, lastName=Golden, age=26]
Person [firstName=Peter, lastName=Jones, age=23]
Person [firstName=David, lastName=Paul, age=22]
Print all lastNames beginning with a ‘D’
Person [firstName=John, lastName=David, age=25]
Person [firstName=John, lastName=Doe, age=25]
Print all person with the firstname beginning with ‘J’
Person [firstName=John, lastName=David, age=25]
Person [firstName=John, lastName=Doe, age=25]
Person [firstName=Joseph, lastName=Golden, age=26]
Java 8 Streaming
package java8streaming;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Optional;
import java.util.function.BinaryOperator;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
public class JavaCount {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Employee> empList = new ArrayList<>();
empList.add(new Employee (101, “John”, 101, “active”, 51000));
empList.add(new Employee (103, “Doe”, 102, “inactive”, 90000));
empList.add(new Employee (104, “Joseph”, 102, “active”, 210002));
empList.add(new Employee (105, “Golf”, 101, “active”, 331003));
//Display employee details based on dept
Map<Integer, List<Employee>> empListBasedOnDept = empList.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Employee::getDeptId, Collectors.toList()));
empListBasedOnDept.entrySet().forEach( entry -> {
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + “—” + entry.getValue());
});
//Display and count departments
Map<Integer, Long> empCountDept = empList.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Employee::getDeptId, Collectors.counting()));
empCountDept.entrySet().forEach( entry -> {
System.out.println(“dept ” + entry.getKey() + “–” + entry.getValue());
});
//Display number of active and inactive departs
Long activeEmpCount = empList.stream().filter(e -> “active”.equals(e.getStatus())).count();
Long inactiveEmpCount = empList.stream().filter(e -> “inactive”.equals(e.getStatus())).count();
System.out.println(“active emp count ” + activeEmpCount);
System.out.println(“inactive emp count ” + inactiveEmpCount);
//Get maximum and min salaries
Optional<Employee> emp1 = empList.stream().max(Comparator.comparing(Employee::getSalary));
Optional<Employee> emp2 = empList.stream().min(Comparator.comparing(Employee::getSalary));
System.out.println(emp1);
System.out.println(emp2);
//Display highest salary according to depart
Map <Integer, Optional<Employee>> topSalaryDeptWise = empList.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Employee::getDeptId,
Collectors.reducing(BinaryOperator.maxBy(Comparator.comparing(Employee::getSalary)))));
topSalaryDeptWise.entrySet().forEach(entry -> {
System.out.println(“dept ” + entry.getKey() + ” top emp ” + entry.getValue());
});
}
}
Output:
//Display employee details based on dept
101—[Employee [empId=101, empName=John, deptId=101, status=active, salary=51000], Employee [empId=105, empName=Golf, deptId=101, status=active, salary=331003]]
102—[Employee [empId=103, empName=Doe, deptId=102, status=inactive, salary=90000], Employee [empId=104, empName=Joseph, deptId=102, status=active, salary=210002]]
//Display and count departments
dept 101–2
dept 102—2
//Active/inactive employees
active emp count 3
inactive emp count 1
//Max and min salaries
Optional[Employee [empId=105, empName=Golf, deptId=101, status=active, salary=331003]]
Optional[Employee [empId=101, empName=John, deptId=101, status=active, salary=51000]]
//Highest salaries by department
dept 101 top emp Optional[Employee [empId=105, empName=Golf, deptId=101, status=active, salary=331003]]
dept 102 top emp Optional[Employee [empId=104, empName=Joseph, deptId=102, status=active, salary=210002]]
mport java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
public class TestCoding {
//Check if a string is Isogram or not
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(isIsogram(“pen”));
}
static boolean isIsogram(String s) {
boolean isogram = true;
char[] ch = s.toCharArray();
Set<Character> chSet = new HashSet<Character>();
for(Character c : ch) {
if(chSet.contains(c)) {
isogram = false;
}else {
chSet.add(c);
}
}
return isogram;
}
}
//Output: true. Will be false if pen is not there
package recursion;
public class TestRecursion {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println(num(7));
}
public static int num(int n) {
if(n<=1)
return n;
else
return num(n-1)+num(n-2);
}
}
//Output 13 ie 7+6
public class Counting {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
String str =”The Lord is is my shephard”;
List<String> list = Arrays.asList(str.split(” “));
list.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Function.identity(),Collectors.counting()));
Function<String, String> fn=Function.identity();
System.out.println(fn.apply(str));
Map<String, Long> map = list.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Function.identity(),Collectors.counting()));
System.out.println(map);
}
}
//Output
//The Lord is is my shephard
//{The=1, Lord=1, shephard=1, is=2, my=1}
package myProject;
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Multiplication {
public int multiply(int a, int b);
}
package myProject;
public class Multiply {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Multiplication answer=(a,b)->a*b;
System.out.println(answer.multiply(6, 8));
}
}
//Output 48
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
public class Sum {
public static void main (String[] args) {
List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(2, 10, 22,33, 46, 77, 67);
Set<Integer> Set = new HashSet();
list.stream().filter(x->Set.add(x)).collect(Collectors.toSet()).forEach(x->System.out.println(x));
//list.stream().limit(2).forEach(x->System.out.println(x));
//list.stream().skip(4).forEach(x->System.out.println(x));
}}
//Output
22
10
77
46
package person;
public class Employee {
private int empid;
private String empName;
private int deptId;
private String status =”active”;
private int salary;
public Employee(int empid, String empName, int deptId, String status, int salary) {
super();
this.empid = empid;
this.empName = empName;
this.deptId = deptId;
this.status = status;
this.salary = salary;
}
public int getEmpid() {
return empid;
}
public void setEmpid(int empid) {
this.empid = empid;
}
public String getEmpName() {
return empName;
}
public void setEmpName(String empName) {
this.empName = empName;
}
public int getDeptId() {
return deptId;
}
public void setDeptId(int deptId) {
this.deptId = deptId;
}
public String getStatus() {
return status;
}
public void setStatus(String status) {
this.status = status;
}
public int getSalary() {
return salary;
}
public void setSalary(int salary) {
this.salary = salary;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return “Employee [empid=” + empid + “, empName=” + empName + “, deptId=” + deptId + “, status=” + status
+ “, salary=” + salary + “]”;
}
}
package person;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Optional;
import java.util.function.BinaryOperator;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
public class EmployeeProgram {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
List<Employee> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(new Employee(1, “John Doe”, 111, “inactive”, 25000));
list.add(new Employee(2, “Mark Bruce”, 221, “active”, 55000));
list.add(new Employee(3, “Gary King”, 221, “active”, 85000));
list.add(new Employee(4, “Jerry Khan”, 111, “active”, 80000));
list.add(new Employee(5, “Congo Box”, 111, “active”, 66000));
//List all employees by department
//list.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Employee::getDeptId, Collectors.toList()));
Map<Integer, List<Employee>>listBasedOnDept=list.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Employee::getDeptId, Collectors.toList()));
listBasedOnDept.entrySet().forEach(x -> {
System.out.println(x.getKey() + “–” + x.getValue()
);
});
//Counting no. of departments and employees in each department
Map<Integer, Long> empCountDept = list.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Employee::getDeptId, Collectors.counting()));
empCountDept.entrySet().forEach(x-> {
System.out.println(x.getKey() + “–” + x.getValue());
});
//Count active and inactive employees
Long activeEmpCount = list.stream().filter(x -> “active”.equals(x.getStatus())).count();
Long inactiveEmpCount = list.stream().filter(x -> “inactive”.equals(x.getStatus())).count();
System.out.println(“active emp count — ” + activeEmpCount);
System.out.println(“inactive emp count — ” + inactiveEmpCount);
//Print maximum and minimum salaries
Optional<Employee> emp1 =list.stream().max(Comparator.comparing(Employee::getSalary));
Optional<Employee> emp2 =list.stream().min(Comparator.comparing(Employee::getSalary));
System.out.println(emp1);
System.out.println(emp2);
//List department and top salary earners
Map<Integer, Optional<Employee>> topSalaryEmpDept = list.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Employee::getDeptId,
Collectors.reducing(BinaryOperator.maxBy(Comparator.comparing(Employee::getSalary)))));
topSalaryEmpDept.entrySet().forEach(x-> {
System.out.println(“Dept ” + x.getKey() + ” topEmp ” + x.getValue());
});
}
}
//Output
221–[Employee [empid=2, empName=Mark Bruce, deptId=221, status=active, salary=55000], Employee [empid=3, empName=Gary King, deptId=221, status=active, salary=85000]]
111–[Employee [empid=1, empName=John Doe, deptId=111, status=inactive, salary=25000], Employee [empid=4, empName=Jerry Khan, deptId=111, status=active, salary=80000], Employee [empid=5, empName=Congo Box, deptId=111, status=active, salary=66000]]
221–2
111–3
active emp count — 4
inactive emp count — 1
Optional[Employee [empid=3, empName=Gary King, deptId=221, status=active, salary=85000]]
Optional[Employee [empid=1, empName=John Doe, deptId=111, status=inactive, salary=25000]]
Dept 221 topEmp Optional[Employee [empid=3, empName=Gary King, deptId=221, status=active, salary=85000]]
Dept 111 topEmp Optional[Employee [empid=4, empName=Jerry Khan, deptId=111, status=active, salary=80000]]